How to Use ReadyBoost in Vista
Windows ReadyBoost can use storage space on some removable media devices, such as a USB 2.0 flash drive that uses fast memory, to speed up your computer by using it along with the hard drive for your virtual memory when RAM is used up. This will show you how to use the ReadyBoost feature in Vista to help speed up your computer.
For more information about ReadyBoost and USB flash drive requirements, see: Windows Help and How-to: ReadyBoost and the ReadyBoost section here: Windows Administration: Inside the Windows Vista Kernel: Part 2
For more information about ReadyBoost and USB flash drive requirements, see: Windows Help and How-to: ReadyBoost and the ReadyBoost section here: Windows Administration: Inside the Windows Vista Kernel: Part 2
The removable media device must contain at least 256 MB of space to work with Windows ReadyBoost. The recommended amount of space to use for Windows ReadyBoost acceleration is one to three times the amount of RAM installed in your computer.
Here are some tips about what to look for when purchasing a USB 2.0 flash drive you plan to use with Windows ReadyBoost:
- Make sure there is at least one free USB 2.0 port on your computer where you can plug in the flash drive (preferably not on an external USB hub shared with other USB devices).
- Look for a note from the manufacturer that the flash drive is Windows ReadyBoost Compatible. Not all manufacturers list this on their packaging.
- If the flash drive is not labeled as compatible with Windows ReadyBoost, check its specifications to see if it is capable of reading and writing data fast enough. The speed requirements for Windows ReadyBoost are at least 2.5 MB per second throughput for 4 kilobyte (KB) random reads and 1.75 MB per second throughput for 512 KB random writes.
ReadyBoost cannot beat the performance improvement of just adding more RAM though.
Here's How:
1. Plug a USB flash drive or other removable media device into your computer.
NOTE: AutoPlay should now open. If not, see: How to Change AutoPlay Settings in Vista
2. Under General Options, click Speed up my system.
NOTE: This will display the Properties dialog box for your flash drive or other removable media device.
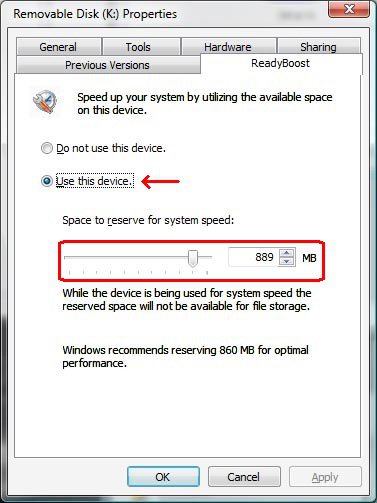
3. Click on the ReadyBoost tab. (See screenshot below step 6)
4. To Turn ReadyBoost Off
NOTE: If this is not already open, then open the Start Menu and click on Computer, right click on the drive used for ReadyBoost and click on Properties, and click on the ReadyBoost tab.
A) Click Do not use this device.
B) Go to step 6.
5. To Turn ReadyBoost On
A) Click Use this device, and then move the slider to choose how much of the available space on your flash drive you want to reserve for boosting your system speed.
6. Click on OK to apply.
That's It,
Shawn
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: