How to Enable or Disable the Receive Window Auto Tuning Level in Vista
The TCP receive window size (RWIN) is the amount of data that a TCP receiver (your computer) allows a TCP sender (other internet or local network computer) to send before having to wait for an acknowledgement. After the connection is established, the receive window size is advertised in each TCP segment. Advertising that maximum amount of data that the sender can send is a receiver-side flow control mechanism that prevents the sender from sending data that the receiver cannot handle. A sending host can only send at a maximum the amount of data advertised by the receiver before waiting for an acknowledgment and a receive window size update. Auto Tuning adjusts the receive windows size continually based upon the changing network conditions. This usually happens if you have a network device (EX: Router, modem, etc.) that doesn’t support RFC 1323 “TCP Extensions for High Performance”.
The TCP window size field controls the flow of data and is limited to between 2 and 65,535 bytes, and cannot be expanded anymore. Thus, a scaling factor is used to get a larger TCP receive window size to achieve more efficient use of high bandwidth networks. The TCP window scale option is used to increase the maximum window size from 65,535 bytes to 1 Gigabyte. Scaling up to larger TCP congestion window sizes is a part of what is necessary for TCP Tuning.
When dealing with slow network performance in Vista, the problem may be due to the above mentioned TCP Window Scaling option, where many older routers and and packet firewalls do not properly implement TCP Window Scaling (doesn’t support RFC 1323), and rewrite the window scaling factor during a transmission, and causing sending and receiving sides to assume different TCP window sizes. The situation causes malfunction Internet connection, non-stable traffic that is very slow, or network connection that is only available intermittently.
Beside, Windows Vista enhances further TCP window scaling with auto tuning feature, where TCP stack in Vista system will auto tune and adjust the RWIN size to increase the percentage of full-sized TCP segments that are used during bulk data transmission based on the network scenario it encountered. And thus it’s no longer possible to specify a custom size for the TCP/IP Receive Window (RWIN) size with the inclusion of new auto tuning feature, unless the application it self uses SO_RCVBUF. However, Vista TCP auto tuning feature may get things wrong sometimes. Instead of optimal true receive window size, incompatible and out of range RWIN size may be used.
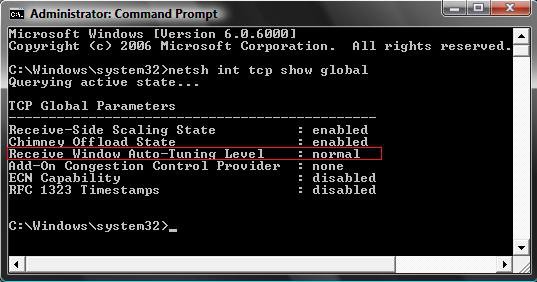
By default, Vista in normal auto tuning level will use RWIN size of 256 bytes with a scale factor of 8. This value is not suitable for all routers and servers which does not support TCP scale factor, and continue to communicate with 65536 bytes.
UPDATE: An Update on Windows TCP AutoTuningLevel - Windows 10 Forums
When dealing with slow network performance in Vista, the problem may be due to the above mentioned TCP Window Scaling option, where many older routers and and packet firewalls do not properly implement TCP Window Scaling (doesn’t support RFC 1323), and rewrite the window scaling factor during a transmission, and causing sending and receiving sides to assume different TCP window sizes. The situation causes malfunction Internet connection, non-stable traffic that is very slow, or network connection that is only available intermittently.
Beside, Windows Vista enhances further TCP window scaling with auto tuning feature, where TCP stack in Vista system will auto tune and adjust the RWIN size to increase the percentage of full-sized TCP segments that are used during bulk data transmission based on the network scenario it encountered. And thus it’s no longer possible to specify a custom size for the TCP/IP Receive Window (RWIN) size with the inclusion of new auto tuning feature, unless the application it self uses SO_RCVBUF. However, Vista TCP auto tuning feature may get things wrong sometimes. Instead of optimal true receive window size, incompatible and out of range RWIN size may be used.
By default, Vista in normal auto tuning level will use RWIN size of 256 bytes with a scale factor of 8. This value is not suitable for all routers and servers which does not support TCP scale factor, and continue to communicate with 65536 bytes.
UPDATE: An Update on Windows TCP AutoTuningLevel - Windows 10 Forums
Possible TCP/IP Auto Tuning Related Problems:
- Indefinite delay (hang) when opening the Certificate Services snap-in.
- Slow (sometimes no) group policy application.
- Trying to select a domain user in order to add that principal to a local security group (the object picker) would hang indefinitely.
- Instant Messaging is not working well. Sometimes not at all by not being able to sign in.
- Access to local file servers (EX: networked drives, etc.) are extremely slow and sometimes did not succeed at all (appears to hang).
- Internet connection problems.
- Extremely slow file transfers.
- Other strange unexplained network connecting issues.
- Wireless network connection problems
- Website browsing and downloads are extremely slow.
 FIRST
FIRST 
1. Open a elevated command prompt.
2. Click on Continue in the UAC prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type in bold belowand press Enter. (See screenshot below)
netsh interface tcp show global
4. Close the command prompt when done.
5. Run through the steps below to see if you have a TCP/IP Auto Tuning issue
 STEP ONE
STEP ONE 
1. Open a elevated command prompt.
2. Click on Continue in the UAC prompt.
3. To Restrict Auto Tuning
NOTE: Allows for the receive window to grow beyond the default value of 65,535 bytes, but limits such growth in some scenarios.
A) In command prompt, type in bold below and press Enter. (See screenshot below)
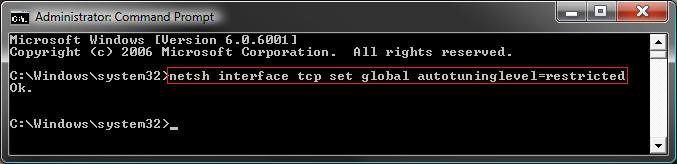
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=restricted
B) You will get a OK response if successful. If not, repeat step 3A.
C) Go to step 5.
4. To Highly Restrict Auto Tuning
NOTE: Allows for the receive window to grow beyond the default value of 65,535 bytes, but doing so very conservatively. In this mode, Vista will by default use a RWIN of 16,384 bytes with a scale factor of 2.
A) In the command prompt, type in bold below and press Enter. (See screenshot below)
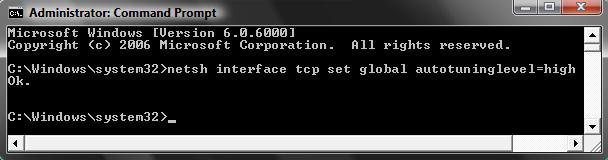
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=high
B) You will get a OK response if successful. If not, repeat step 4A.
5. Close the command prompt window and restart the computer to apply the changes.
6. If it fixed your problem stop here. If not, continue to Step Two below.
 STEP TWO
STEP TWO 
NOTE: Disables the autotunning feature in Vista completely, and sets and locks the RWIN receive window to the default value as 65536 bytes.
1. Open a elevated command prompt.
2. Click on Continue in the UAC prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type in bold belowand press Enter. (See screenshot below)
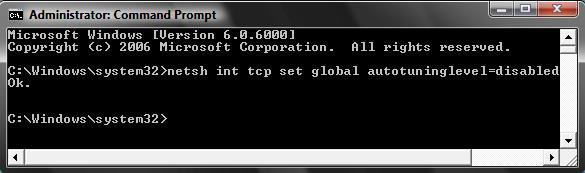
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled
You can also type in bold below and press enter after each command:
- netsh
- interface
- tcp
- set heuristics disabled
- set global autotuninglevel=disabled
- exit
4. You will get a OK response. If not, repeat step 3.
5. Close the command prompt and restart the computer to apply the changes.
6. If it fixed your problem stop here. If not, you may not have a issue with Auto Tuning and will need to turn it back on. Continue to Step 3 below.
 STEP THREE
STEP THREE 
NOTE: This turns Auto Tuning back to the default on (Normal) setting in Vista. Allows for the receive window to grow to accommodate almost all scenarios. See NOTE at the top of the tutorial for more on this.
1. Open a elevated command prompt.
2. Click on Continue in the UAC prompt.
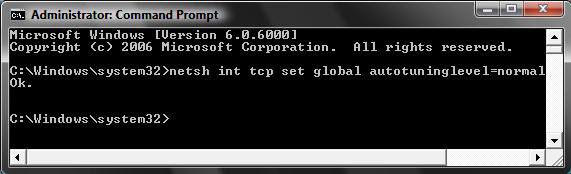
3. In the command prompt, type in bold below and press Enter. (See screenshot below)
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=normal
You can also type in bold below and press enter after each command:
- netsh
- interface
- tcp
- set heuristics enabled
- set global autotuninglevel=normal
- exit
4. You will get a OK response if successful. If not, repeat step 3.
5. Close the command prompt and restart the computer to apply the changes.
That's it,Shawn
Related Tutorials
- How to See and Flush the Contents of the DNS Resolver Cache in Vista
- How to Fix the Windows Live Messenger Unable to Sign In Error in Vista
- How to Change or Disable the QoS Reserved Bandwidth Limit in Vista
- How to Create a Local Area Network Connection Status Shortcut in Vista
- How to Create a Network Connections Shortcut in Vista
- How to Enable or Disable the Chimney Offload State in Vista
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: