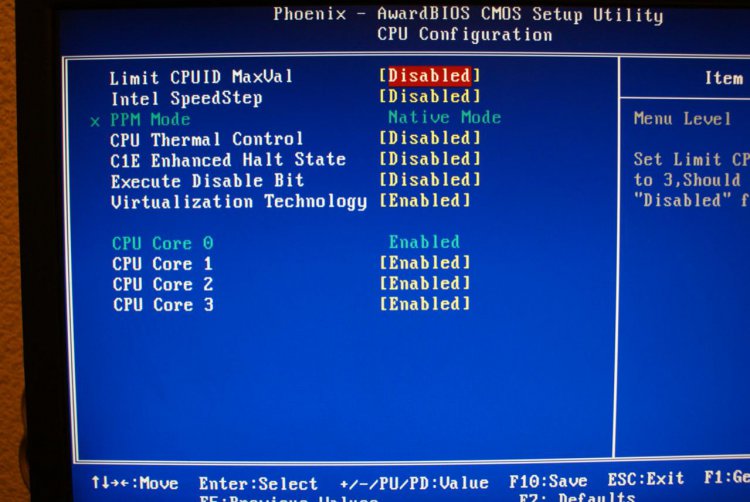
C1E - Enhanced Halt State
"Whenever the OS executes the halt instruction, the CPU enters what is known as the halt state. Architecturally, what's going on in a halt state is the clock signal is shut off to the CPU for some period of time. With no clock signal, none of the logic in the chip will do anything and thus power consumption is reduced. Performance is also significantly reduced; however, the halt instruction isn't usually called during application usage, so the performance aspects of the halt state aren't very important.
The problem with the halt state is that it does nothing to reduce voltage, only current draw by stopping clocks from going to the CPU. Since Power varies linearly with both current and voltage (P = I * V), you're effectively only addressing half of the problem. The Enhanced Halt State, as Intel calls it, does two things: it reduces the clock speed of the CPU by decreasing the clock multiplier down to its minimum value (on the EE 965 series, that's 14x, or 2.8GHz), then reducing the voltage. The clock speed is reduced and then the voltage is dropped, to maintain stability.
Intel insists that the enhanced halt state is a significantly lower power state than the conventional halt state, thanks to the reduction in voltage in addition to the reduction in clock speed. While the standard halt state causes a linear reduction in power, Intel's enhanced halt state causes an exponential decrease in power, potentially offering better power savings than the standard halt state. The real world impact obviously depends on how idle your system happens to be."
EIST:
"What EIST does is very similar to AMD's Cool'n'Quiet. It is demand based reduction in CPU clock speed and voltage. Using the same mechanism of adjusting clock speed and voltage, based on the application demand, the processor will dynamically increase/decrease its clock speed between its minimum clock and its normal operating frequency, as well as voltage, in order to optimize for power consumption.
Because of the way EIST (and AMD's Cool'n'Quiet) works, there's inherently a drop in performance. The idea is this: if you're performing a task that's not using 100% of the CPU, the CPU will operate at a slightly reduced frequency in order to conserve power. So, while some tasks will require that the system run at full speed, others will run at lower speeds. "


 SK
SK Sorry guys I check its not under Advance options or CPU Configuration
Sorry guys I check its not under Advance options or CPU Configuration